|
|
|
Taxonomic Hierarchy |
|
Kingdom: |
Animalia -- animal |
|
Phylum: |
Arthropoda -- arthropods |
|
Class: |
hexapoda -- insects |
|
Subclass: |
Pterygota -- iwinged insects |
|
Infraclass: |
Palaeoptera-- wing insects |
|
Superorder: |
Odonatoptera -- ancient winged insects |
|
Order: |
Odonata -- Dragonflies and Damselflies |
|
Suborder: |
Anisoptera -- Dragonflies |
|
Family: |
Libellulidae -- Skimmers |
|
Genus: |
Pantala |
|
Species: |
Pantala flavescens |
|
|
Description: |
|
Diet: |
|
Naiad-This
is a medium to large naiad with a length of 15/16 to 1 1/16
inches (24 to 26 mm). It is pale green with light brown
markings. There is a large, rear-facing spine on each side
of the last abdominal segments, but there are no hooks on
the back, as some naiads have. |
|
Naiad-The
naiads feed on a wide variety of aquatic insects, such as
mosquito larvae, other aquatic fly larvae, mayfly larvae,
and freshwater shrimp. They will also eat small fish and
tadpoles. |
|
Adult:
This is a medium to large dragonfly with a length of 1 3/4
to 2 inches (44 to 50 mm), with a fairly wide abdomen. The
thorax and abdomen are orange to brown, and there are no
markings. Each hindwing is almost triangular in shape, with
the broadest part at the base where it attaches to the body. |
Adult-The dragonfly
eats small flying insects, especially mosquitoes which also
use seasonal ponds. They also gather in swarms to feed on
flying ants and termites. |
|
Size: |
|
|
size: medium, length 44 - 51 mm,
wingspan 81 - 91 mm |
|
Range Information: |
|
Habitat: |
|
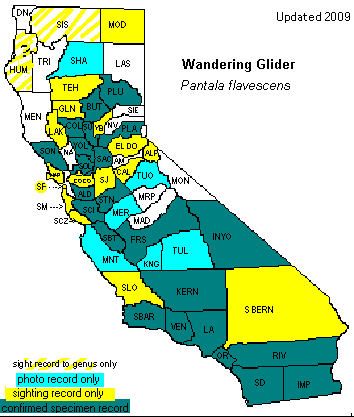
This is
the world's most widely distributed dragonfly. It occurs
worldwide between 400 N and 400 S latitude, and is the only
dragonfly with such a large distribution. It is most common
in tropical and subtropical regions with highly seasonal
rainfall. In Idaho, it occurs at seasonal ponds on the Snake
River Plain.. |
|
This
dragonfly can be found near seasonal ponds. |
|
U. S.
Flight
Season: |
|
California Flight Period: |
|
It has only been observed to fly in August in Idaho, but it
most likely flies over a longer season. |
|
all year in the south, March - December in the north |
|
Ecology: |
|
Reproduction: |
|
The
naiad swims actively about in pursuit of prey, an unusual
trait for naiads of this family. Because they make little
effort to conceal themselves when foraging, the naiads are
very vulnerable to predators such as fish. Luckily, the
seasonal ponds in which they live rarely contain many fish
and the naiads do well. They have voracious appetites and
this results in quick maturation (40 to 60 days, depending
on water temperature and availability of prey). They emerge
as adults synchronously, and the adults migrate using
thermals in the atmosphere. In Idaho, the naiads have been
observed to emerge in early August, indicating that the
migratory adults arrived to breed in June. The adults
migrate around the world in search of seasonal ponds to
reproduce, traveling hundreds or even thousands of miles.
The abdomen of the adult can store large amounts of fat that
is used as energy for long-distance travel. Adults have even
been seen perching on ships far out at sea. The adult
Wandering Glider often forages in large swarms, and one of
the most remarkable reports of such a swarm was of a cloud
of Wandering Gliders that covered 13 square miles (34 square
kilometers)! This is one of the few dragonflies that will
remain on the wing during heavy rain, and in India, its
arrival is said to herald the coming of the monsoons. |
|
After
males and females mate, the female flies with the male
attached (in tandem), to lay her eggs, generally in seasonal
ponds. However, this dragonfly often mistakes the finishes
on shiny new cars for water and lays eggs on them as well, a
most unfortunate choice for the hatching naiads. |
|
Conservation: |
|
Sources : |
|
G1
G2
G3
G4
G5 |
|


|
|
G5 -
Populations are widespread, abundant, and secure.
|
|