|
|
|
 |
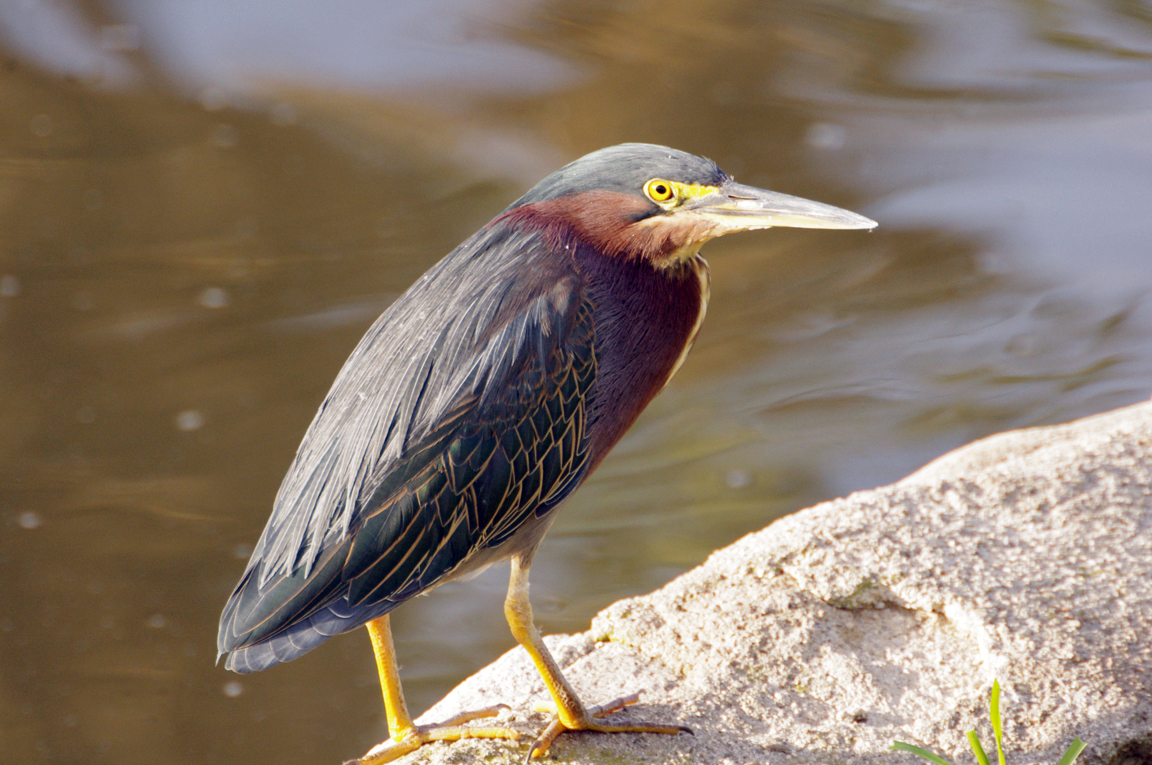
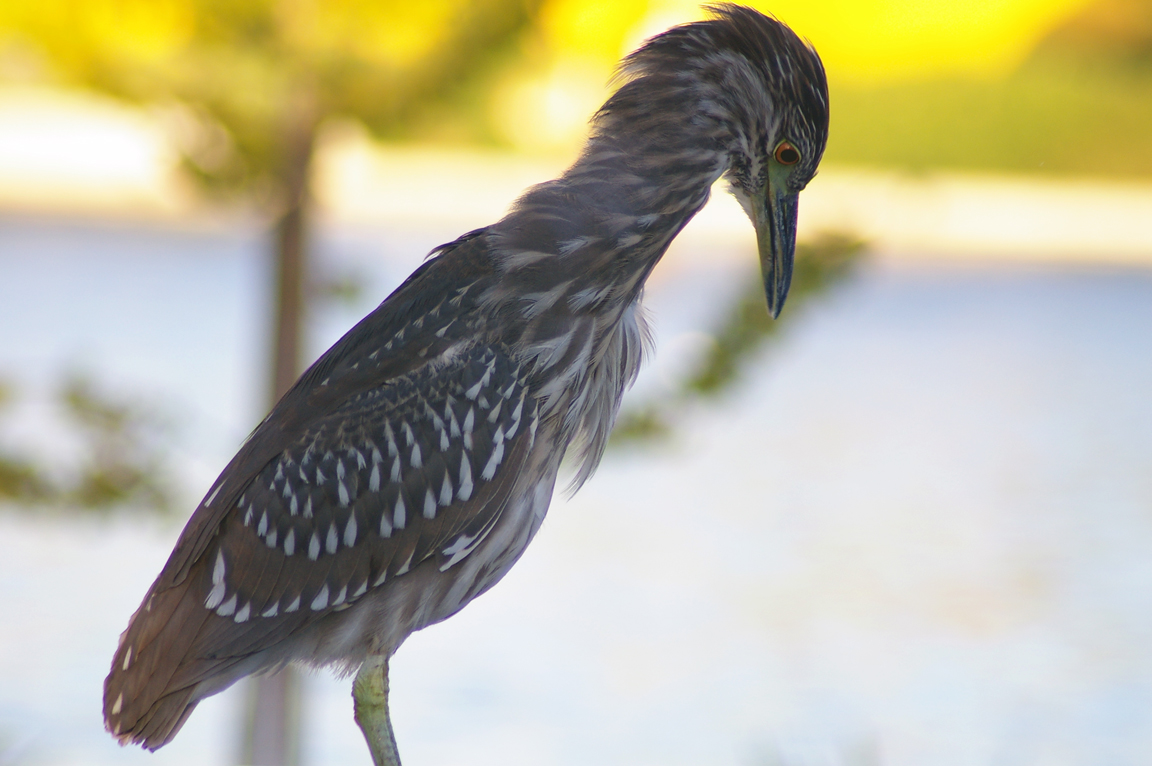
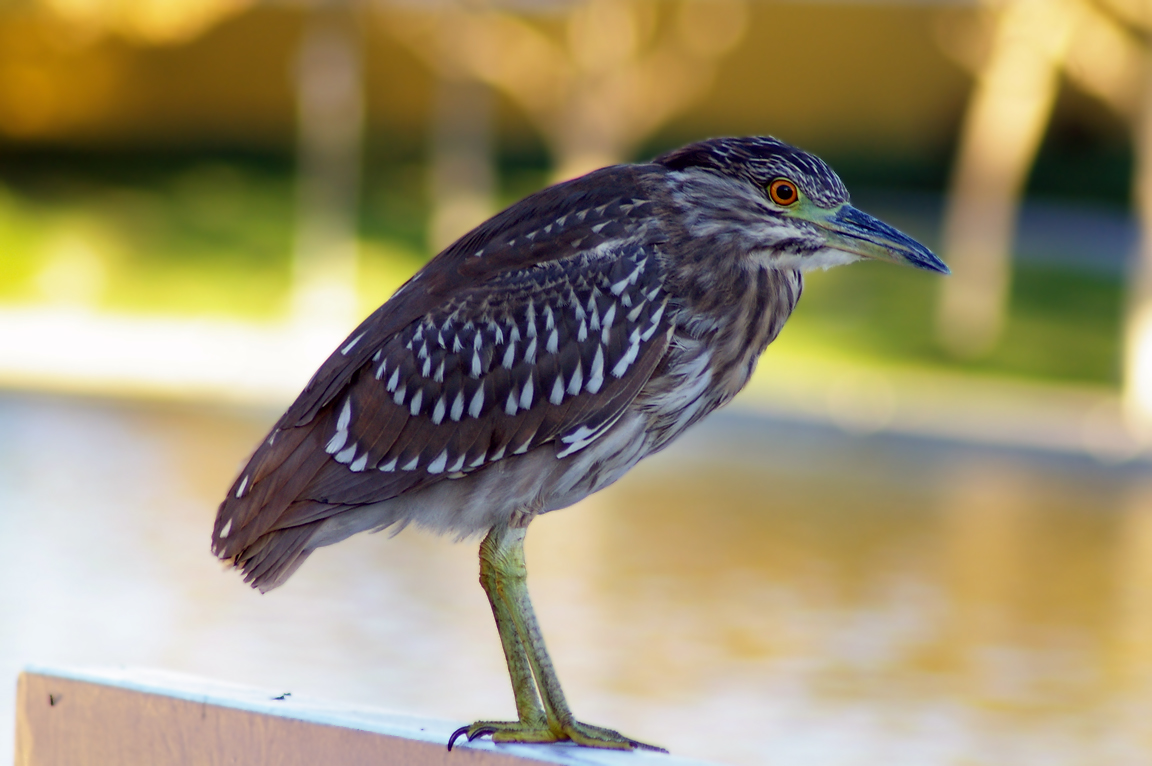
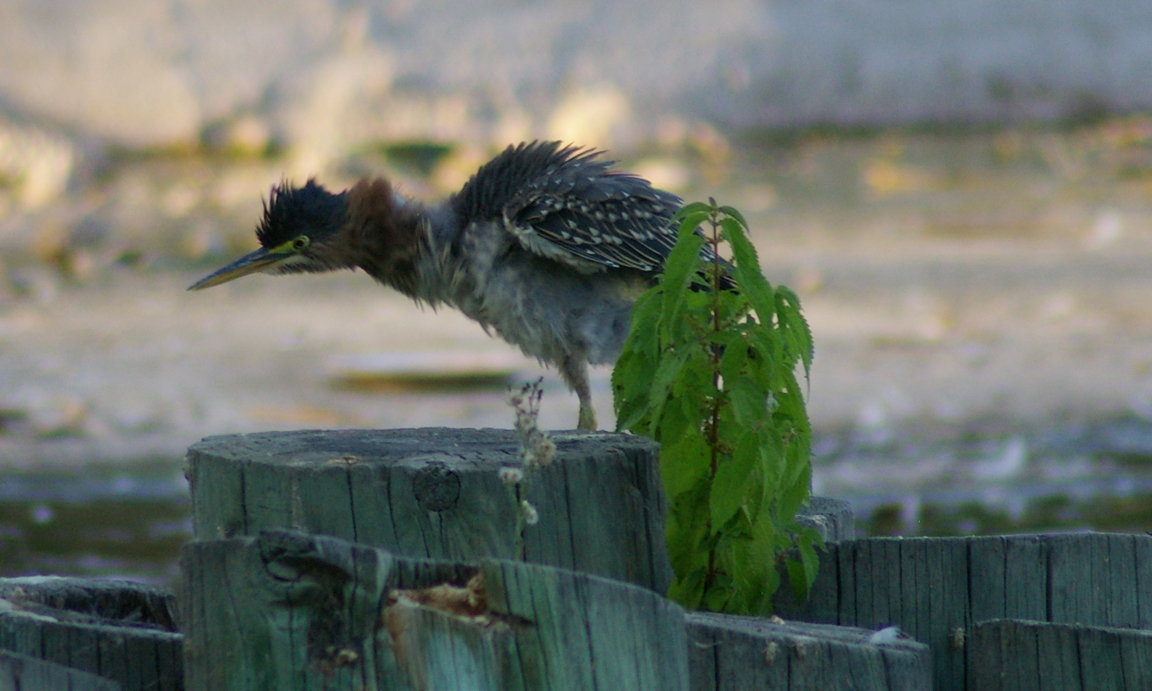
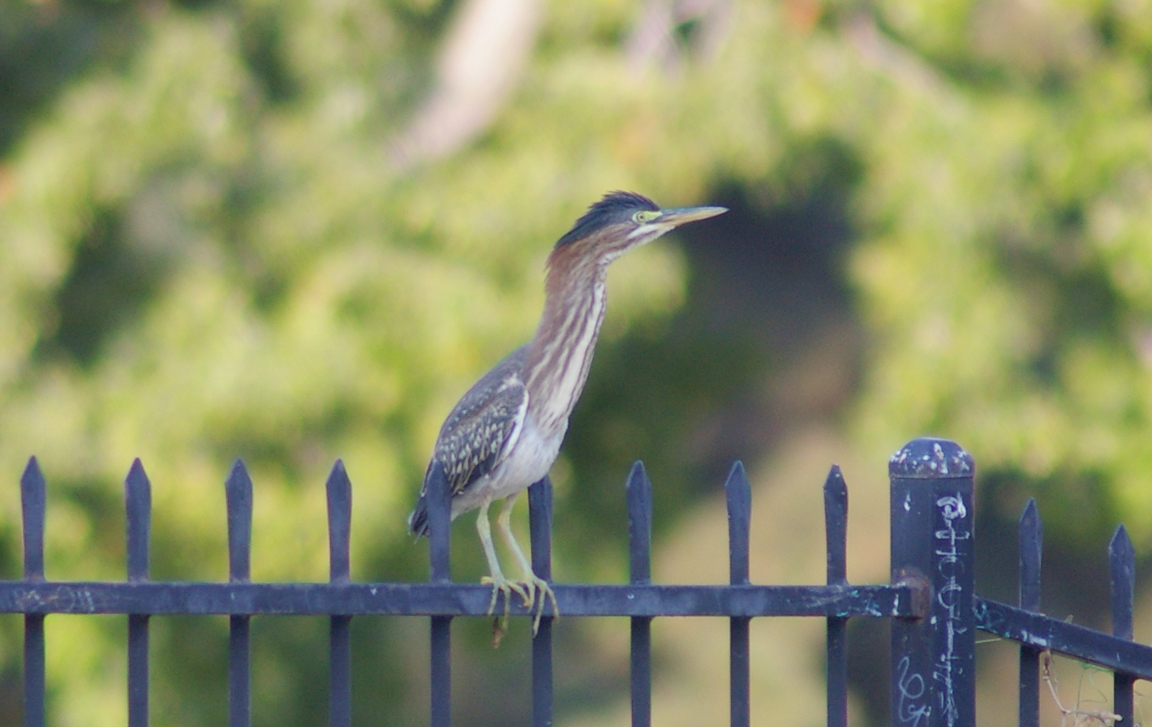
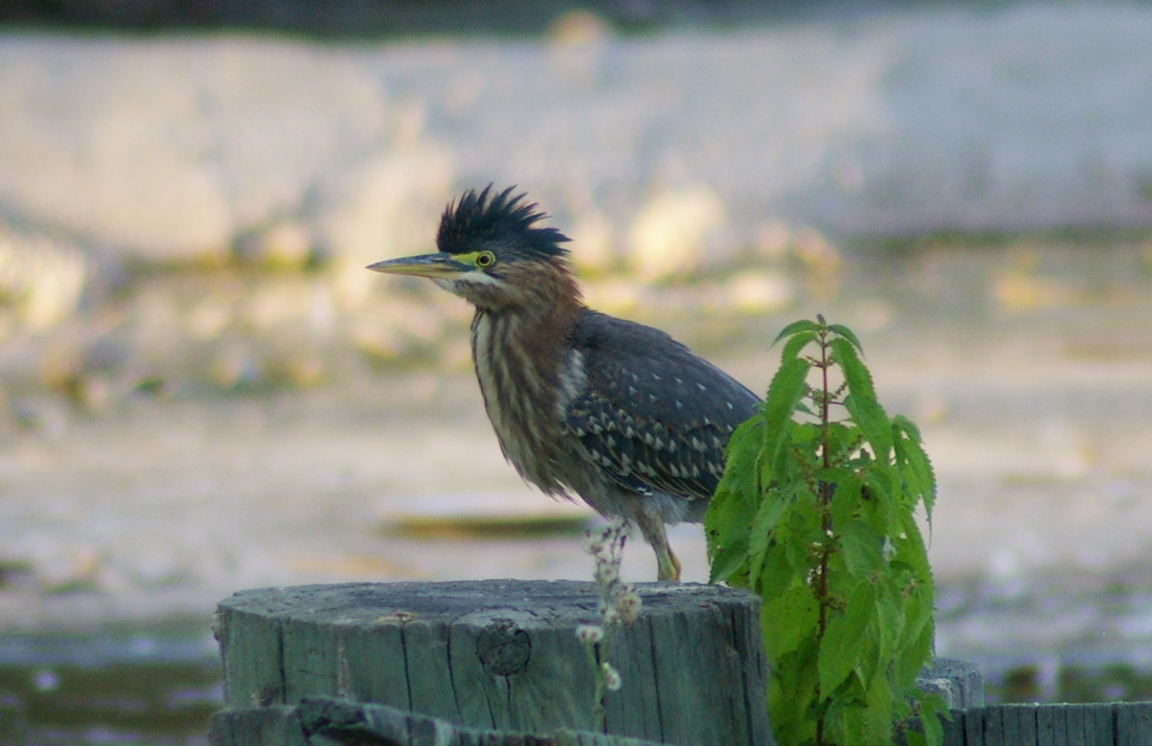
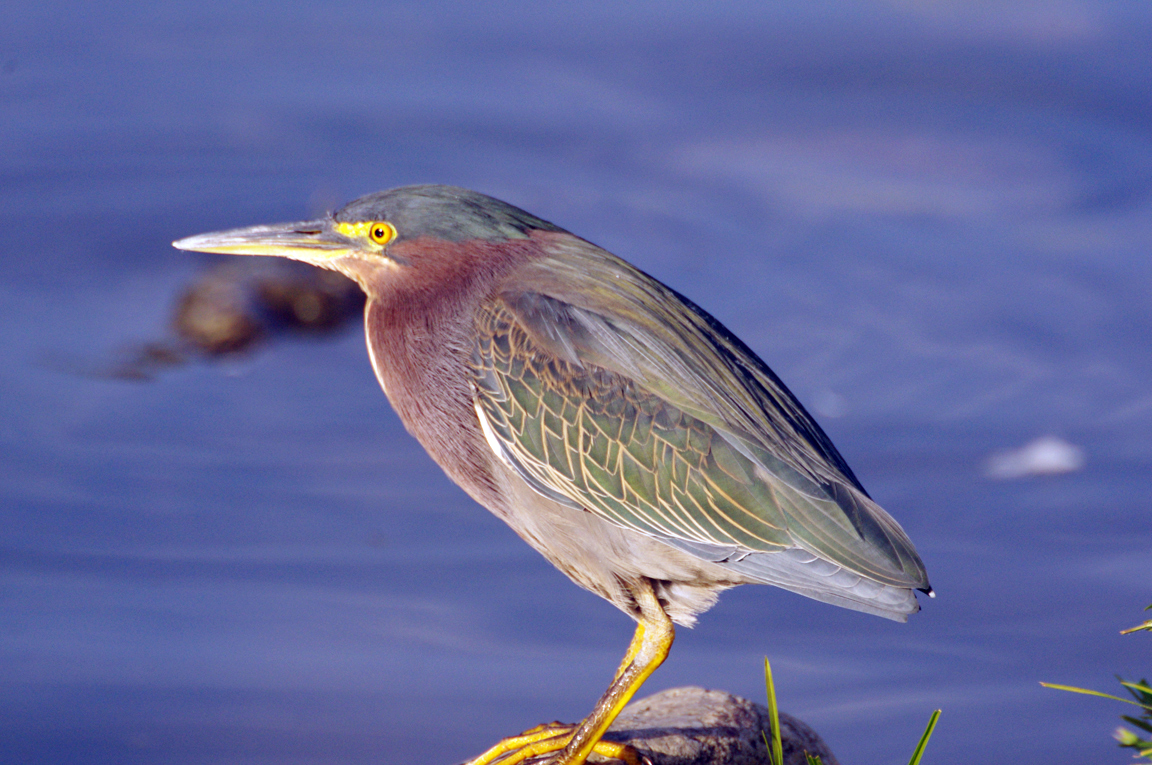
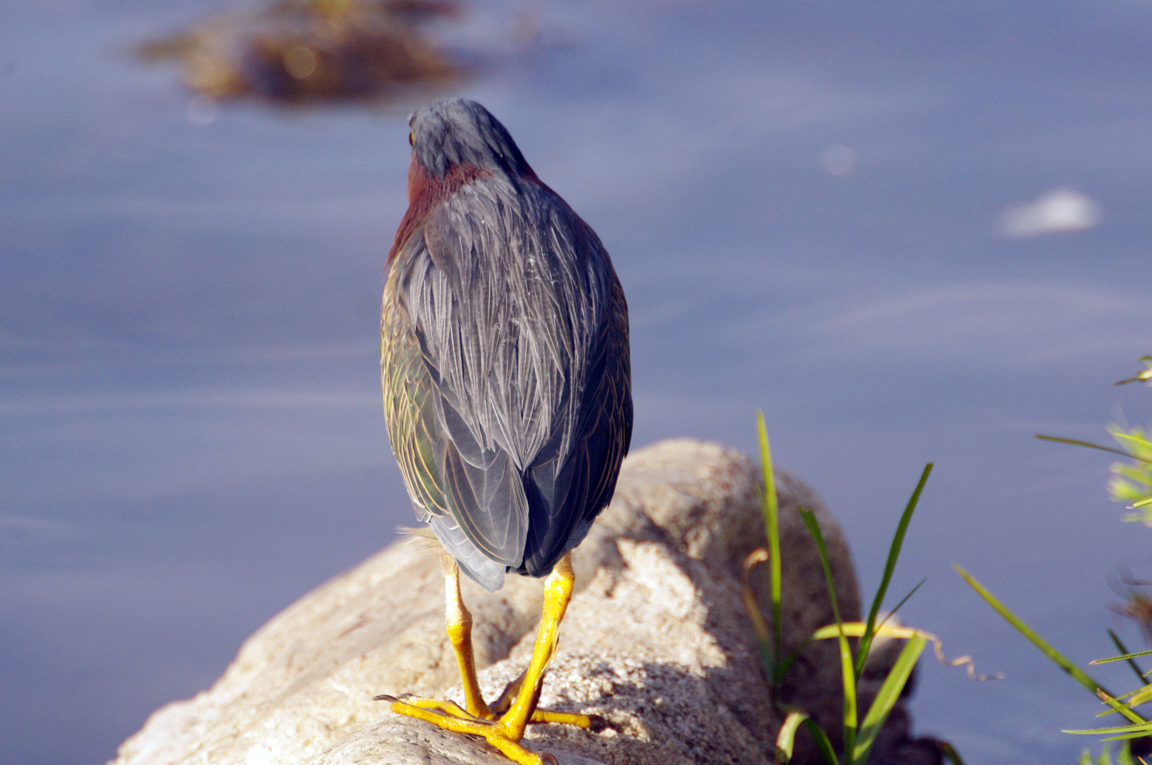
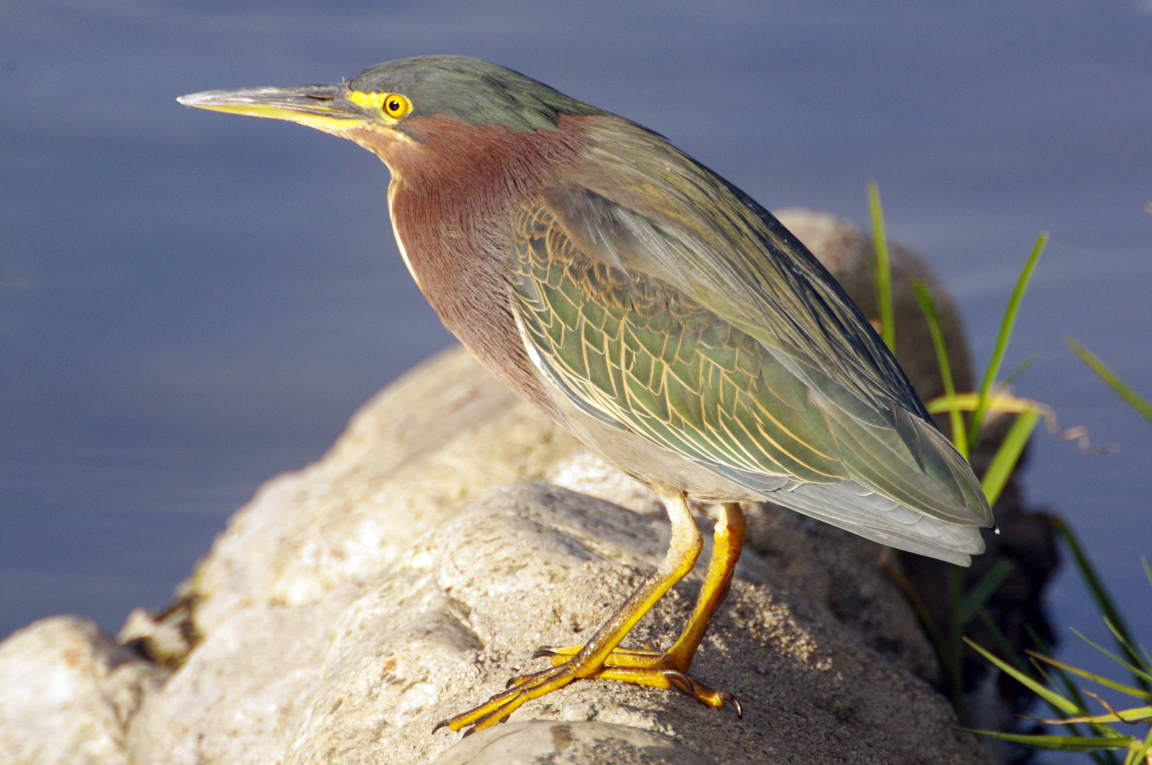
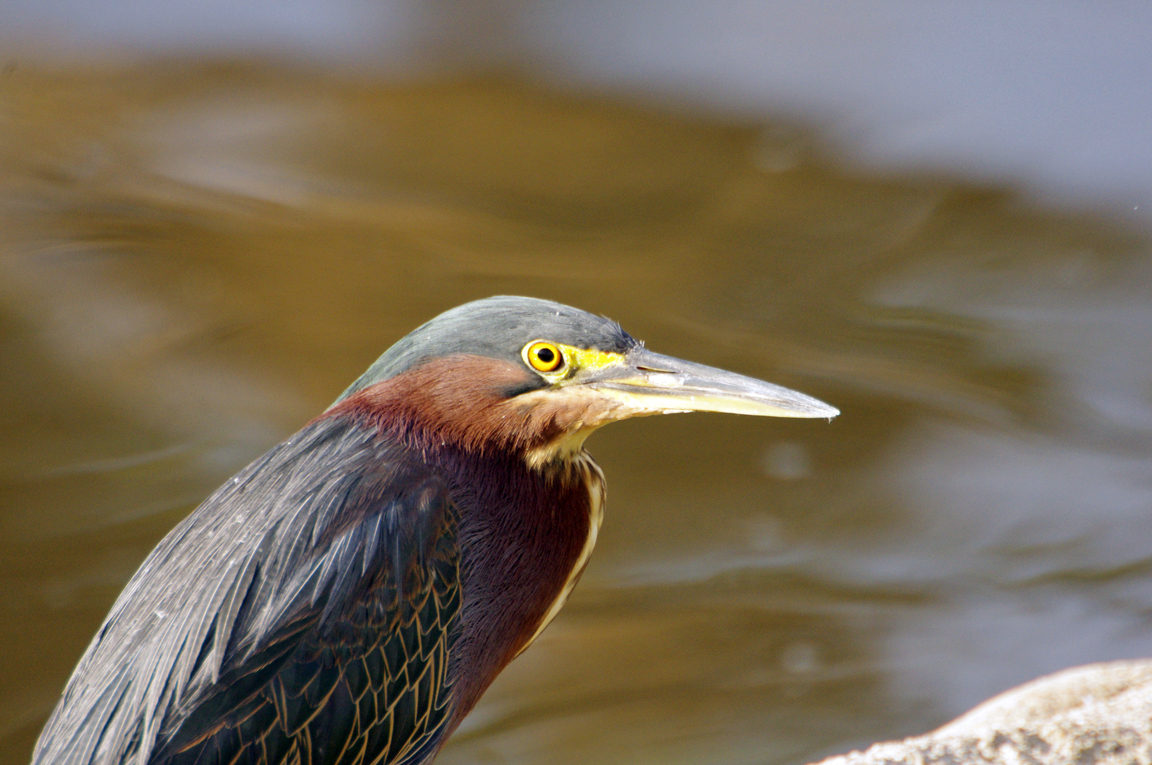
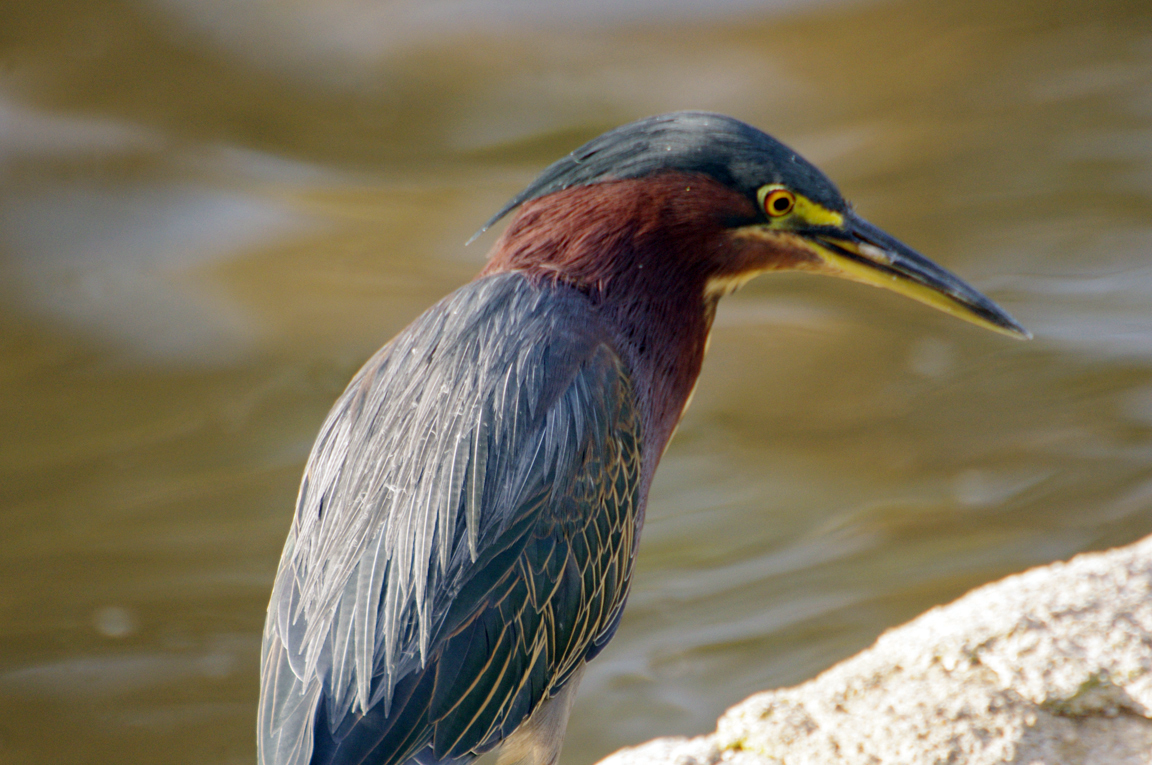
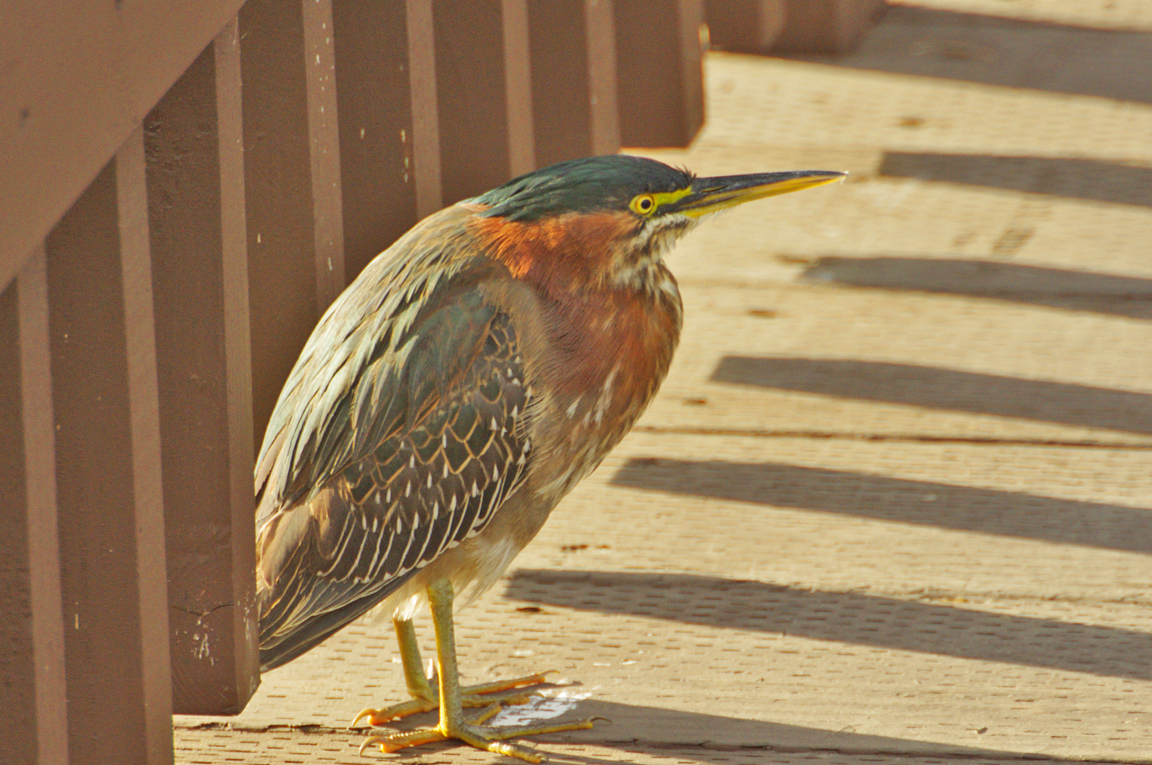
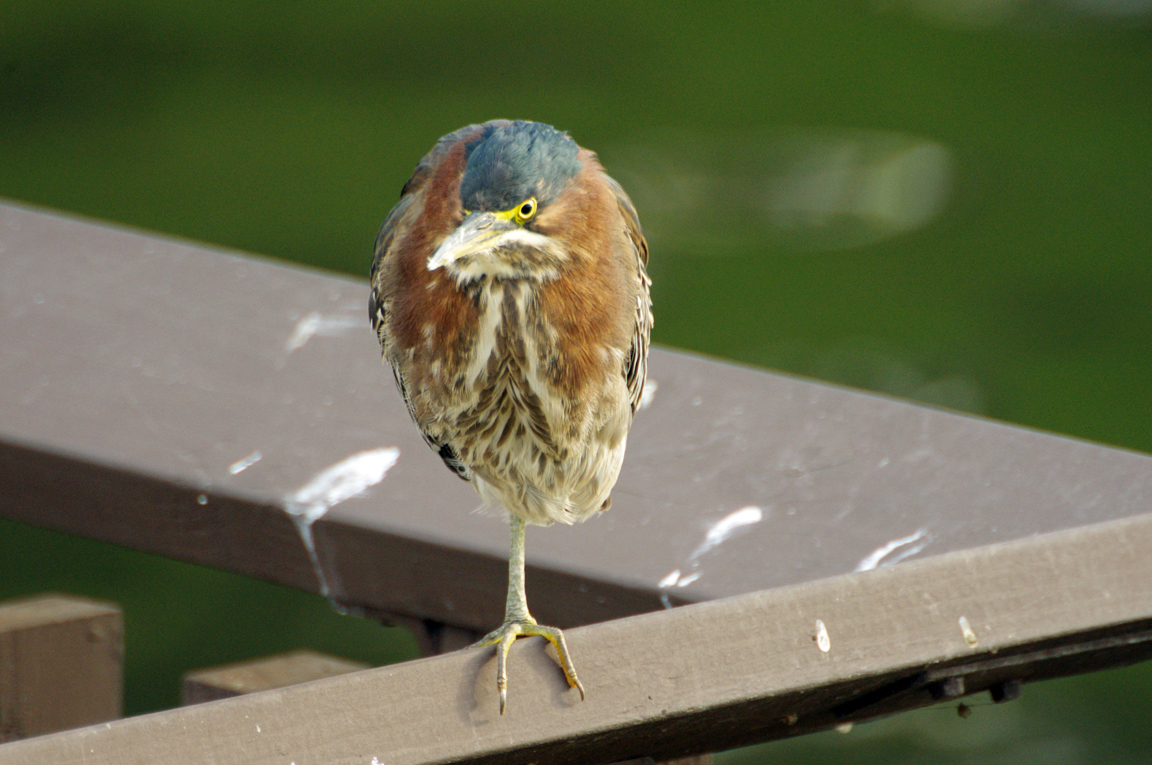
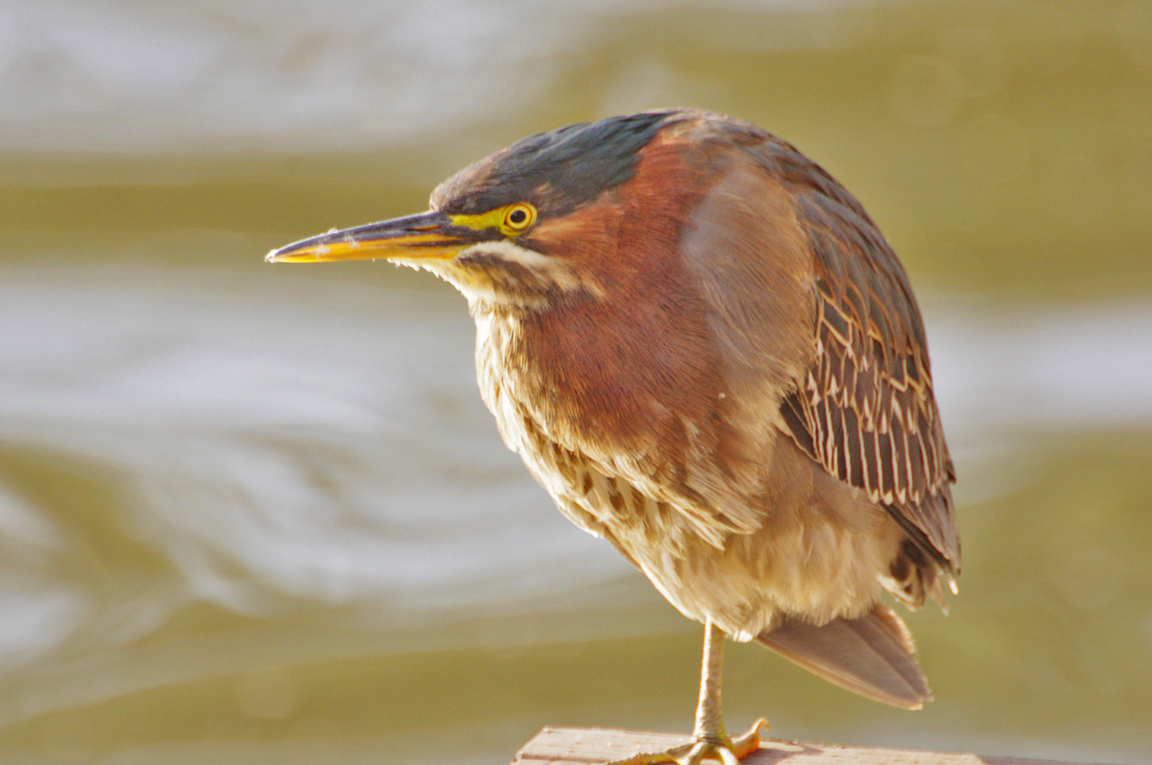
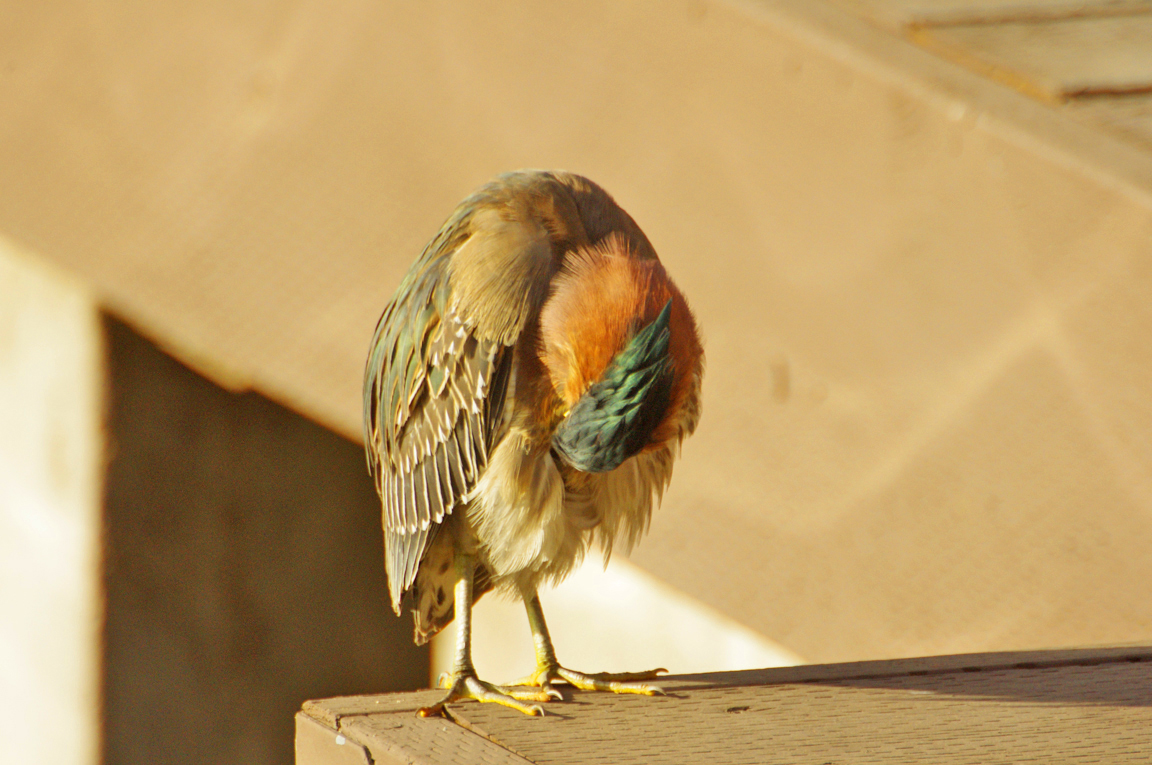
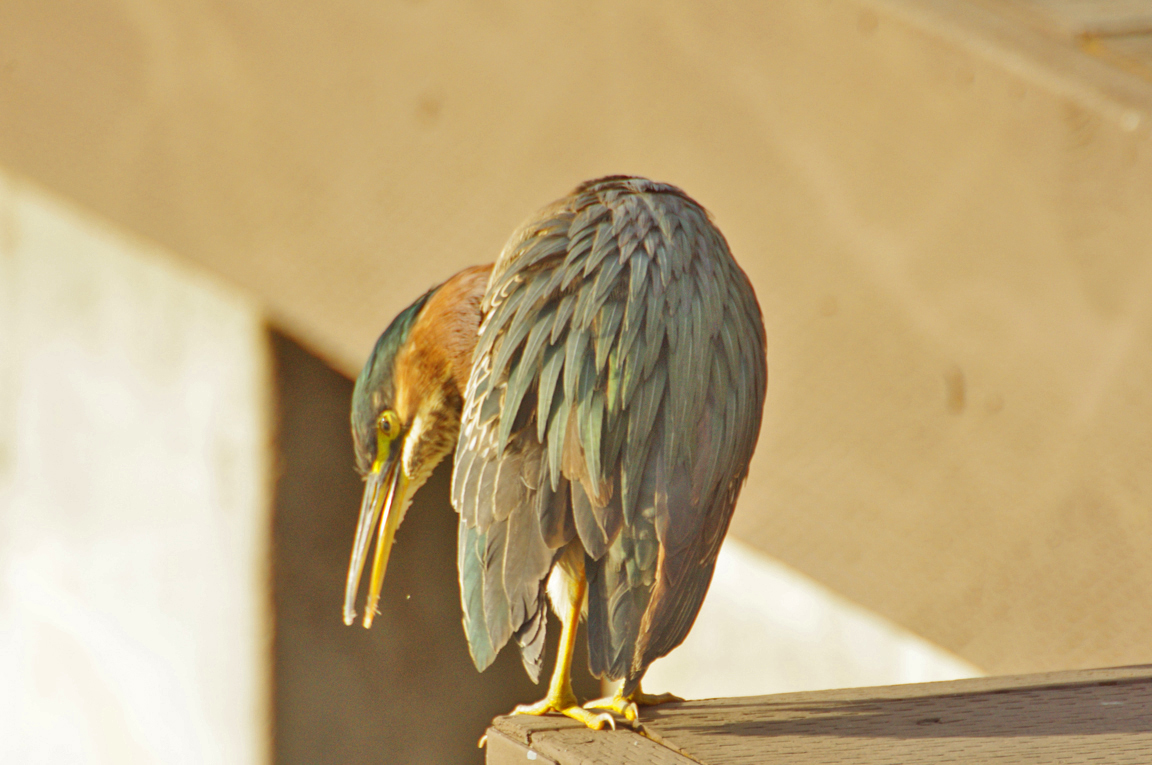
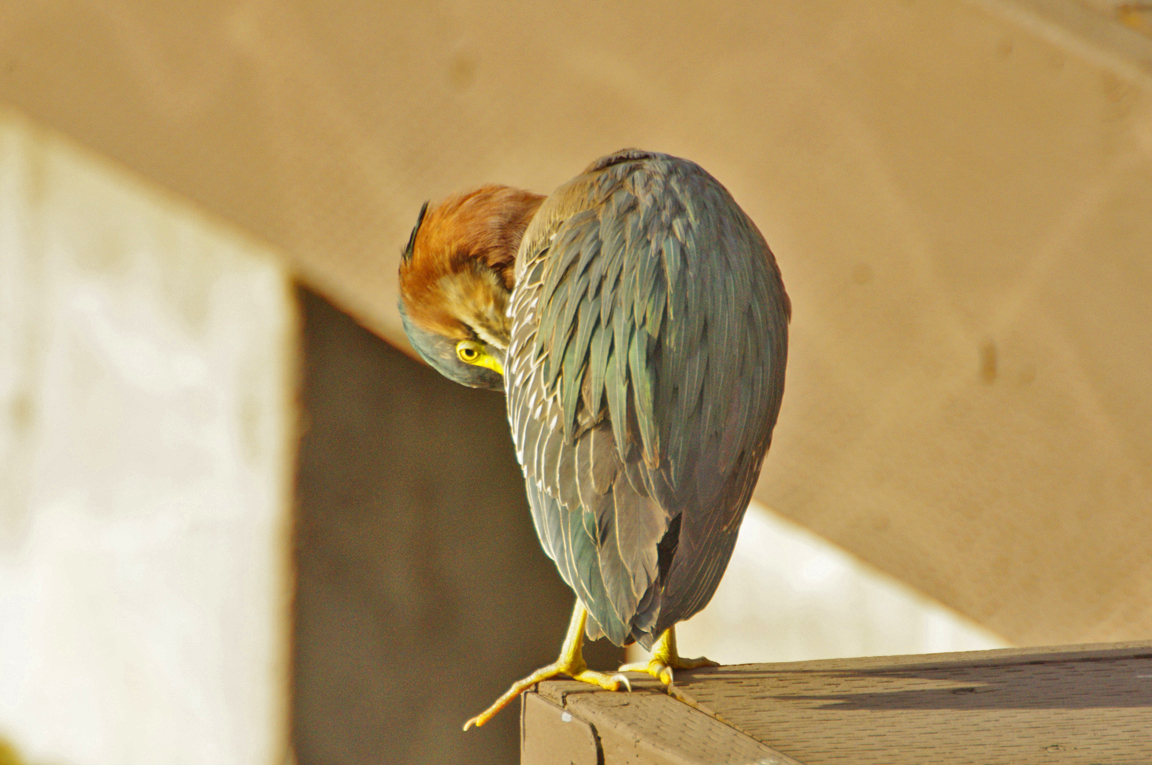
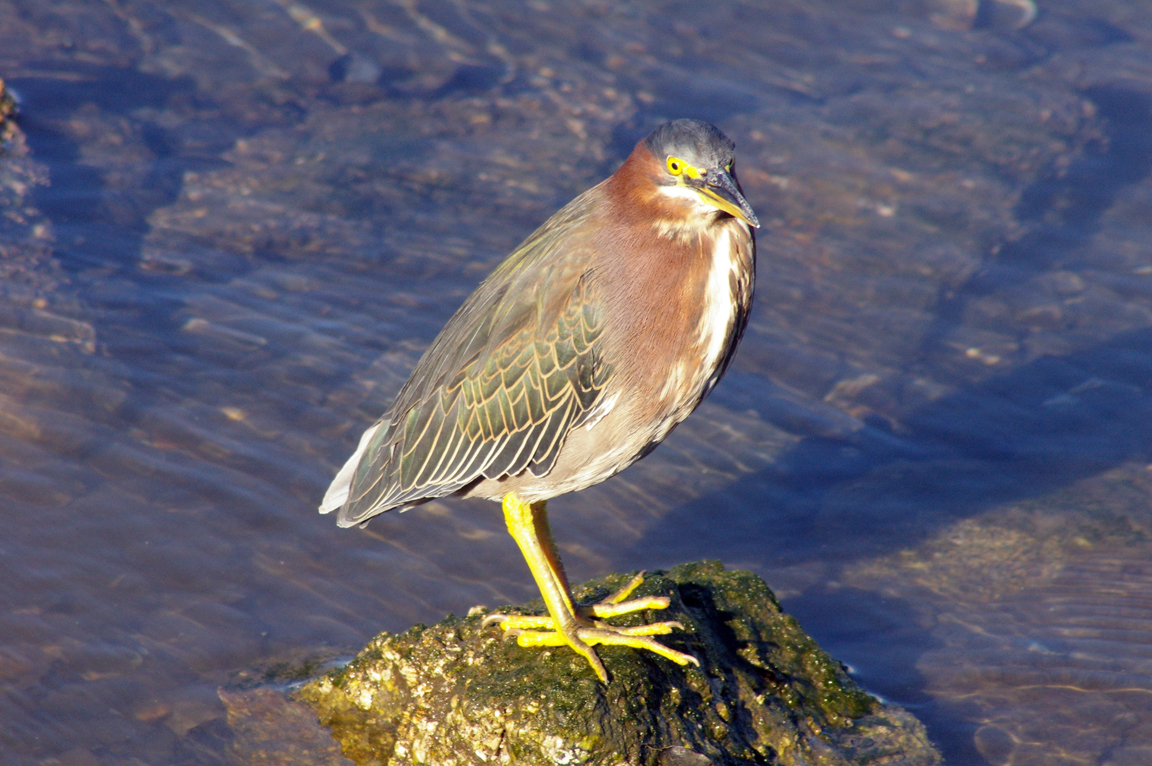
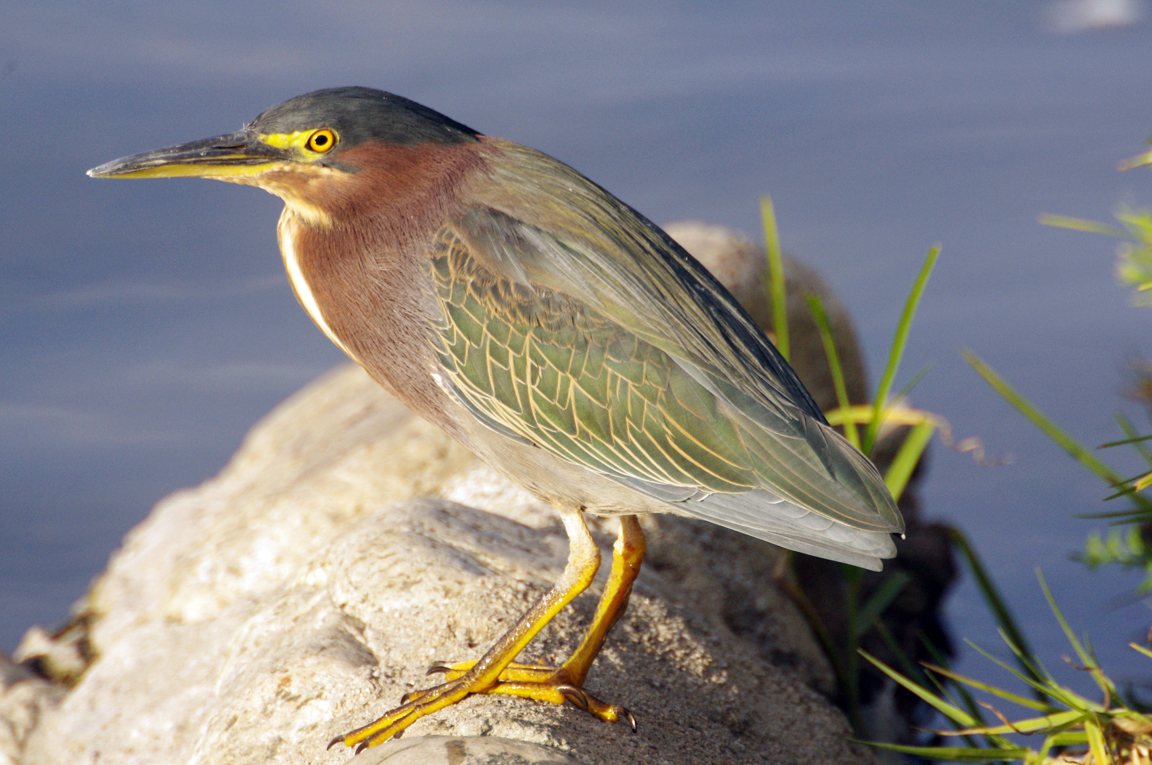
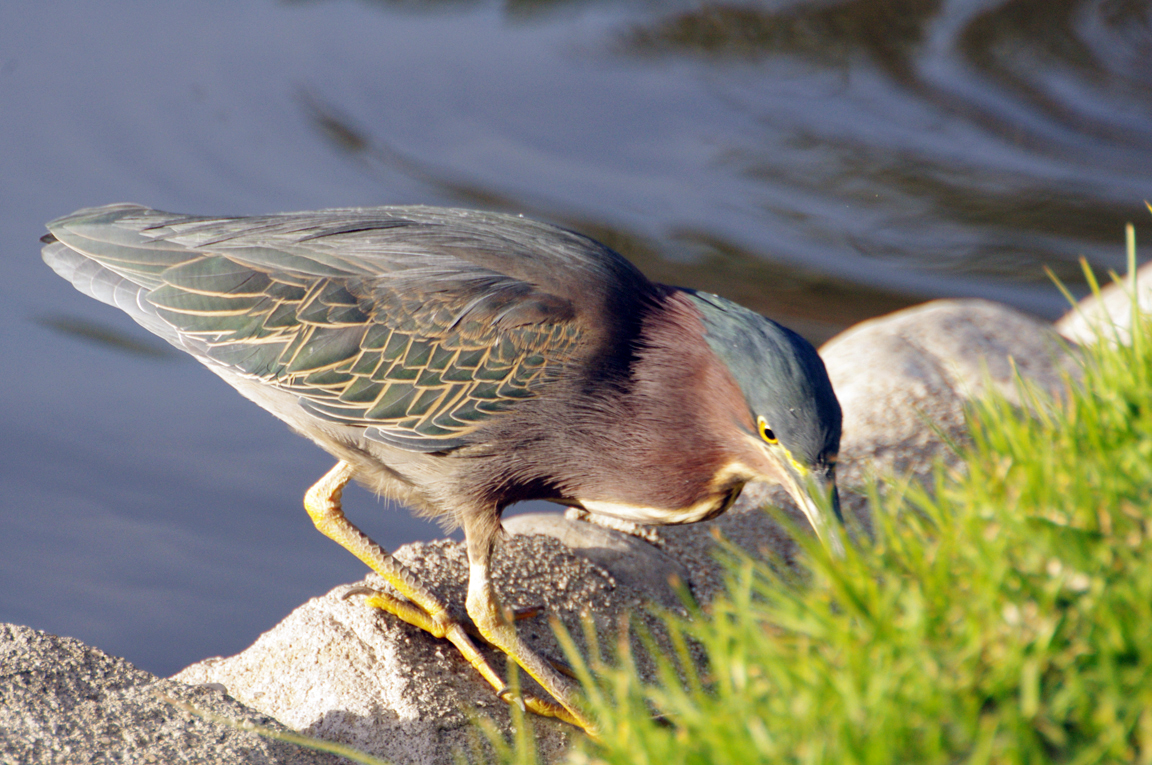
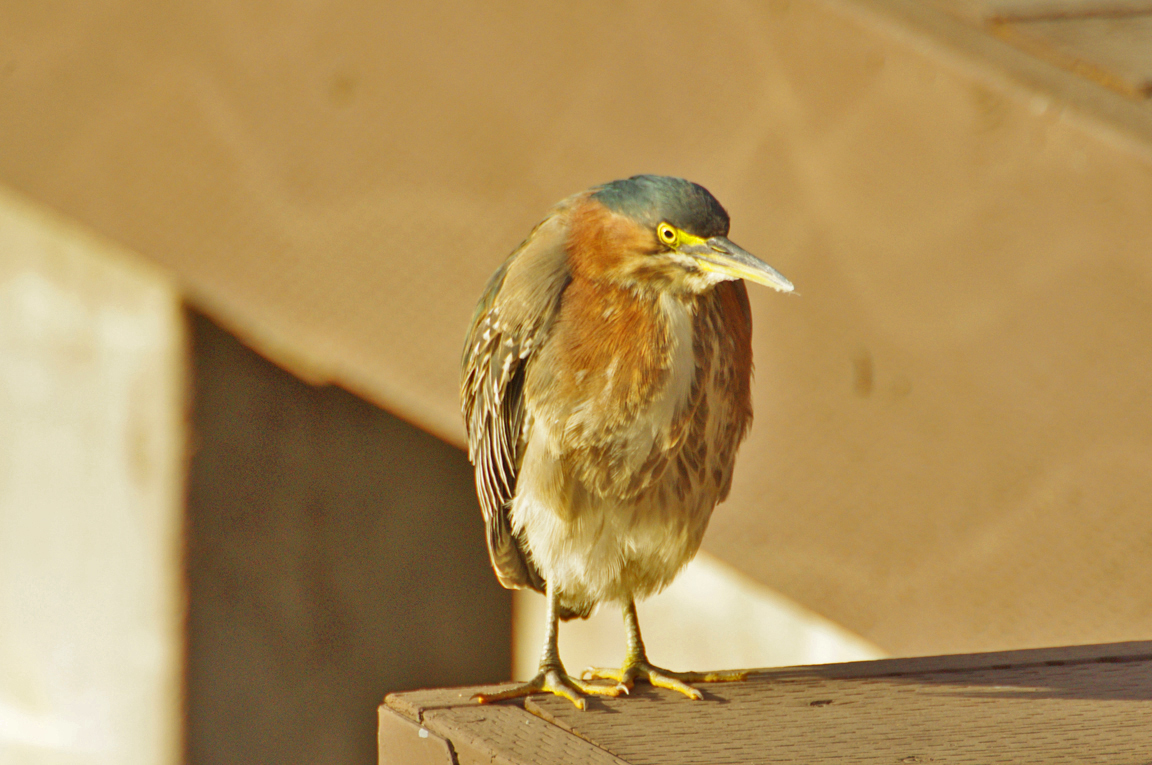
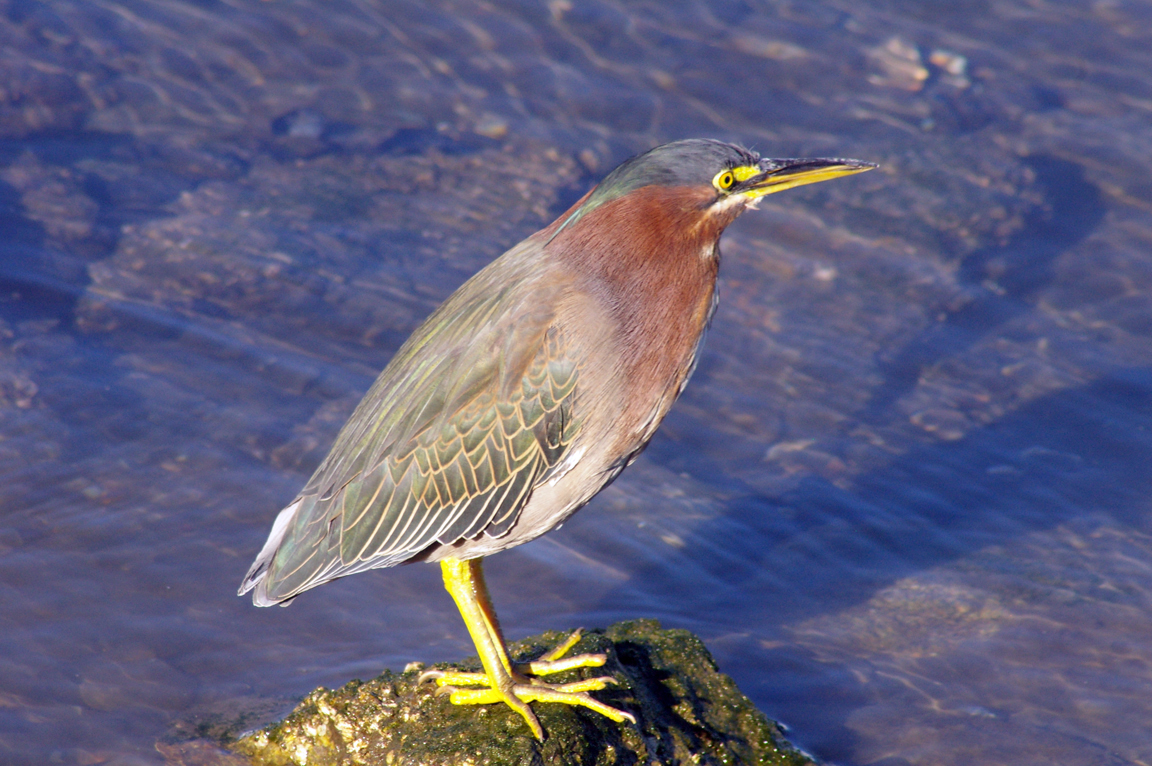
Green Heron
|
| Butorides virescens | |
A small, stocky wading bird, the Green Heron is common in wet spots across much of North America. It can be difficult to see as it stands motionless waiting for small fish to approach within striking range, but it frequently announces its presence by its loud squawking.
Interesting Information
-
The Green Heron is one of the few tool-using birds. It commonly drops bait onto the surface of the water and grabs the small fish that are attracted. It uses a variety of baits and lures, including crusts of bread, insects, earthworms, twigs, or feathers.
-
The Green Heron is part of a complex of small herons that sometimes are considered one species. When lumped, they are called Green-backed Heron. When split, they are the Green Heron, the widespread Striated Heron, and the Galapagos Heron.
-
As is typical for many herons, the Green Heron tends to wander after the breeding season is over. Most wanderers probably seek more favorable foraging areas and do not travel far. But, occasionally some go farther, with individuals going as far as England and France.
Description
Adult Description
-
Size: 41-46 cm (16-18 in)
-
Wingspan: 64-68 cm (25-27 in)
-
Weight: 240 g (8.47 ounces)
-
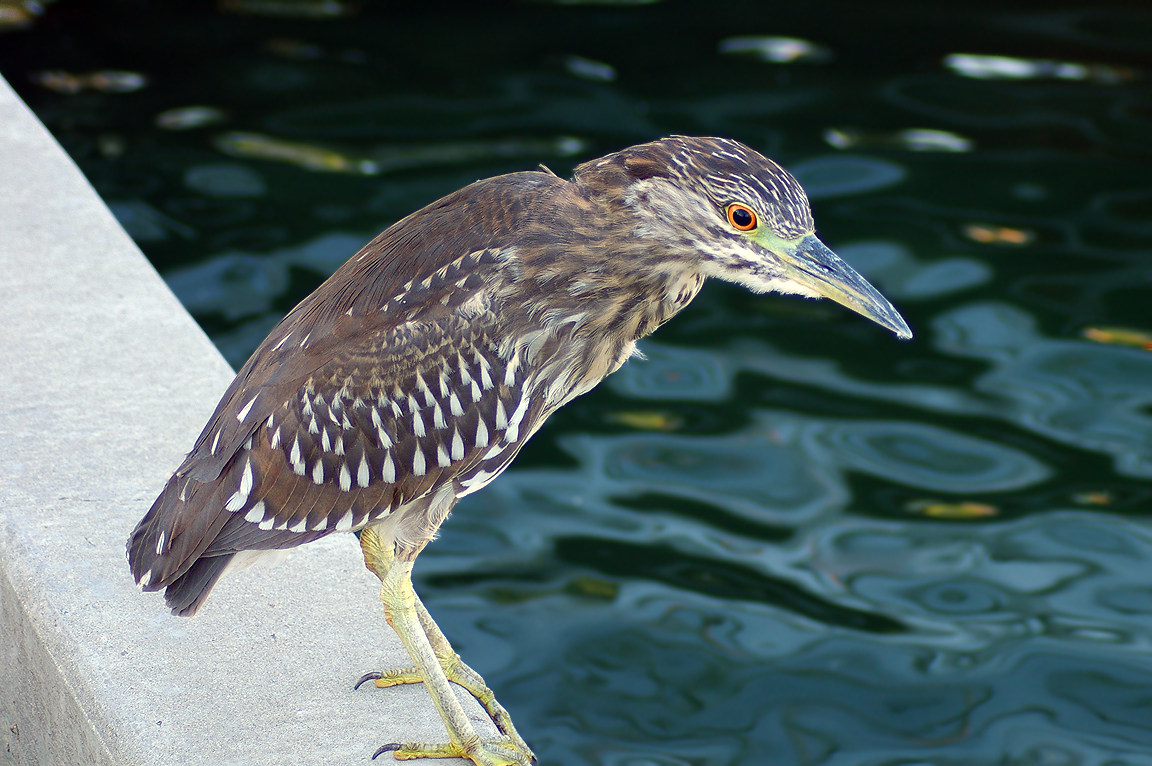
Small, dark heron.
-
Long yellowish legs.
-
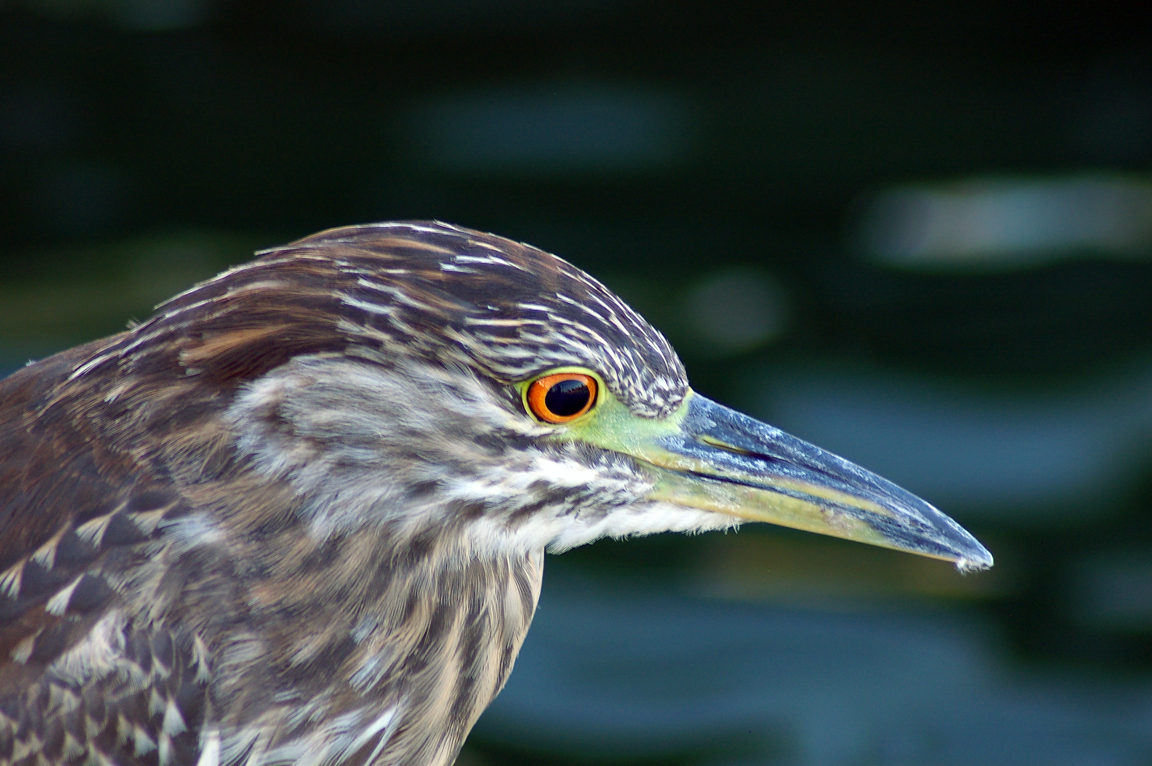
Long, dark, pointed bill.
-
Long neck often kept pulled in tight to body.
-
Legs and neck long, but shorter than most herons.
-
Greenish black cap on head.
-
Wings blackish with greenish or bluish gloss.
-
Neck rufous.
-
Underparts gray.
-
Wing feathers edged in buff.
-
Legs yellow or yellowish orange; glossy orange during breeding.
-
Slight crest can be raised on back of head.
-
Eyes orange or yellow.
Sex Differences
Sexes similar, but female slightly smaller, duller, and lighter.
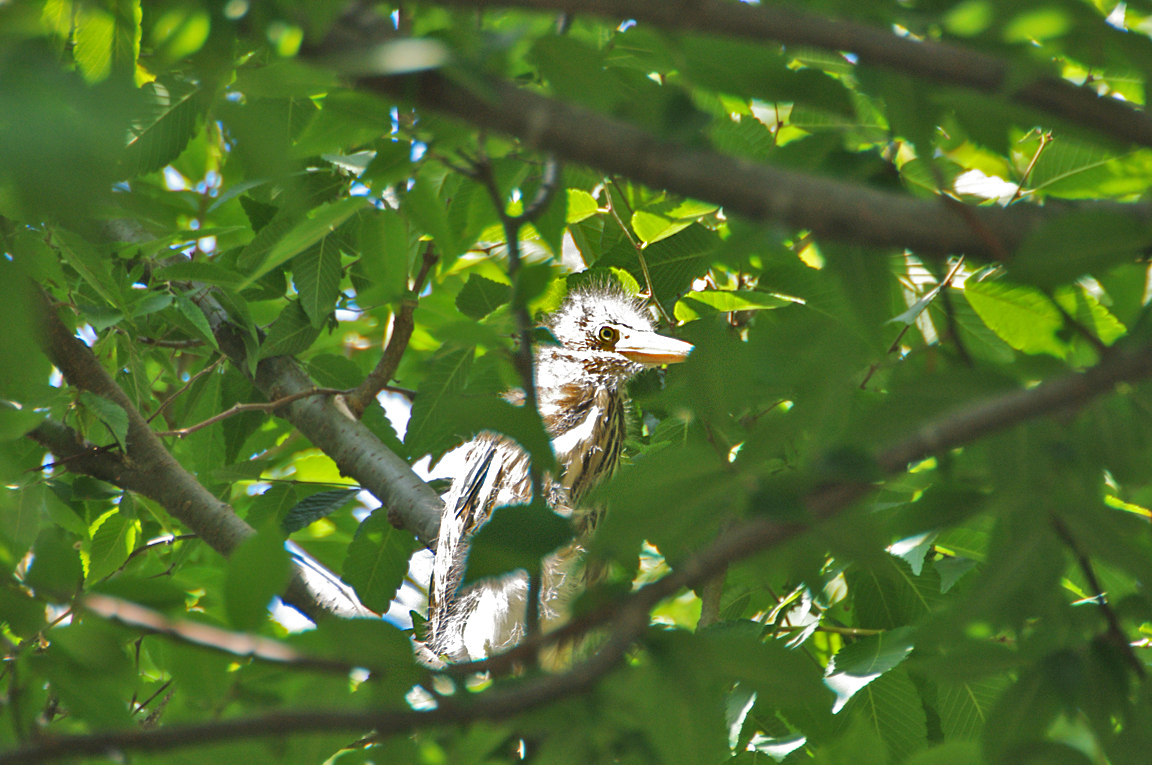
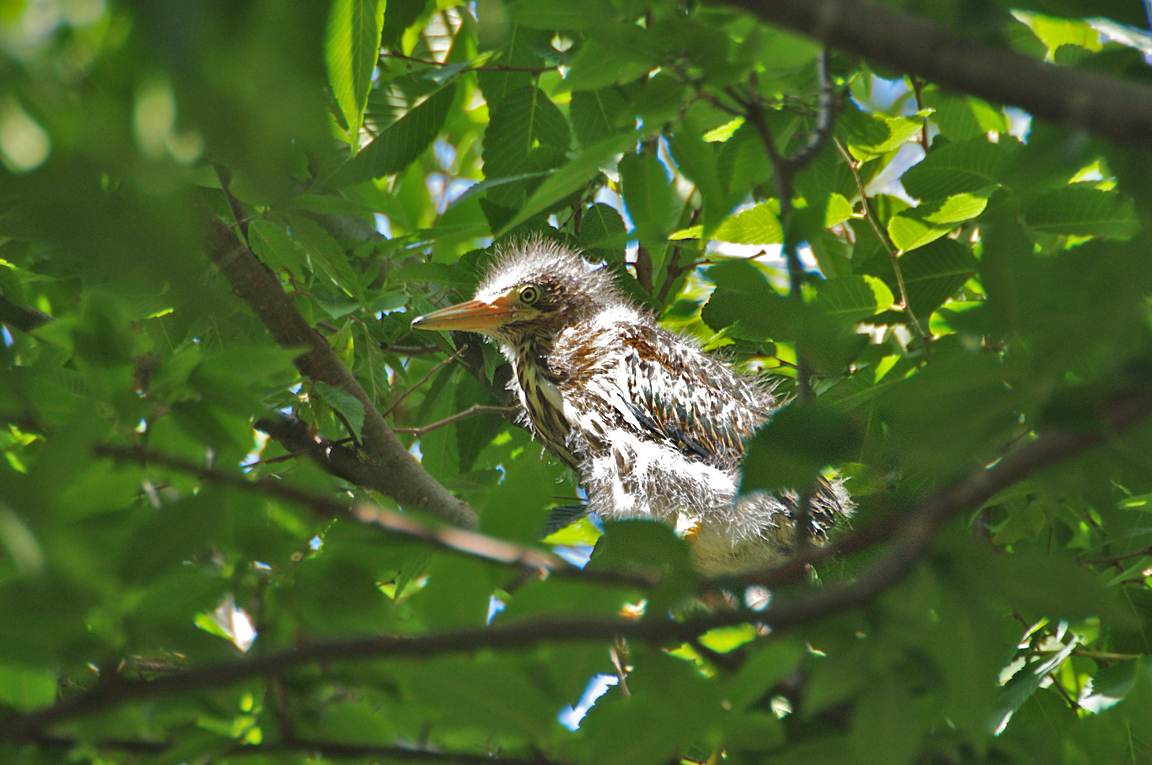
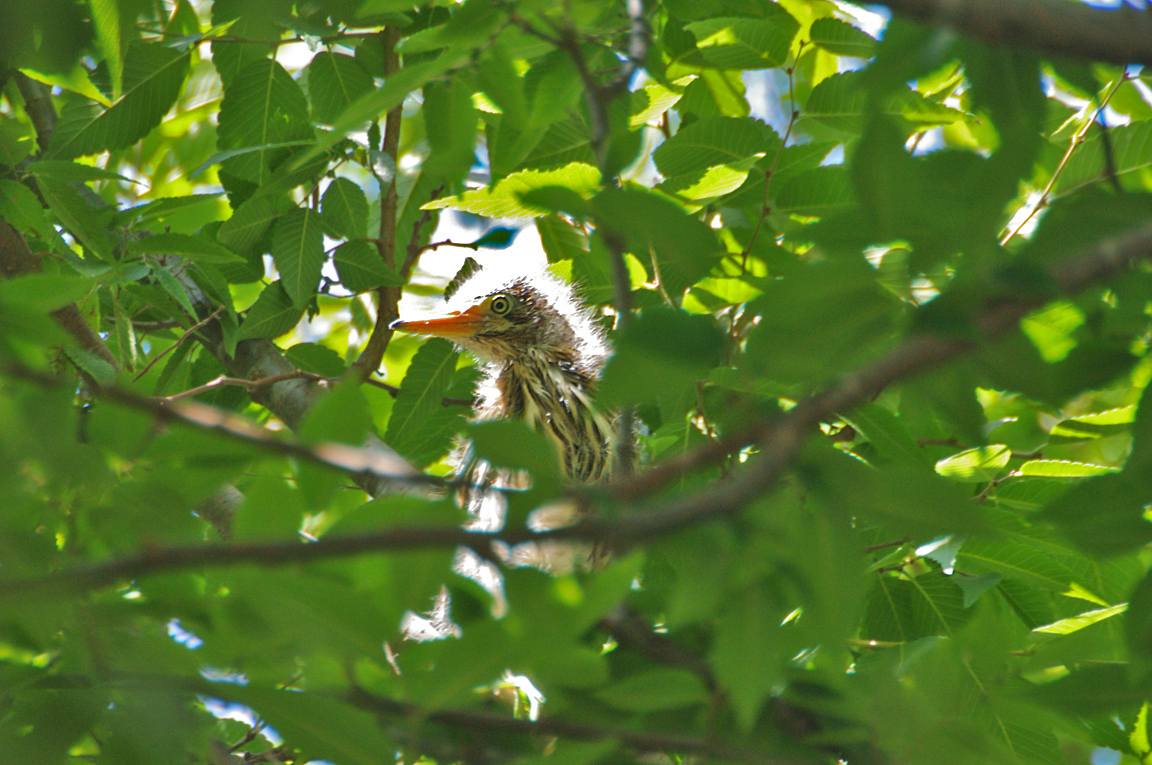
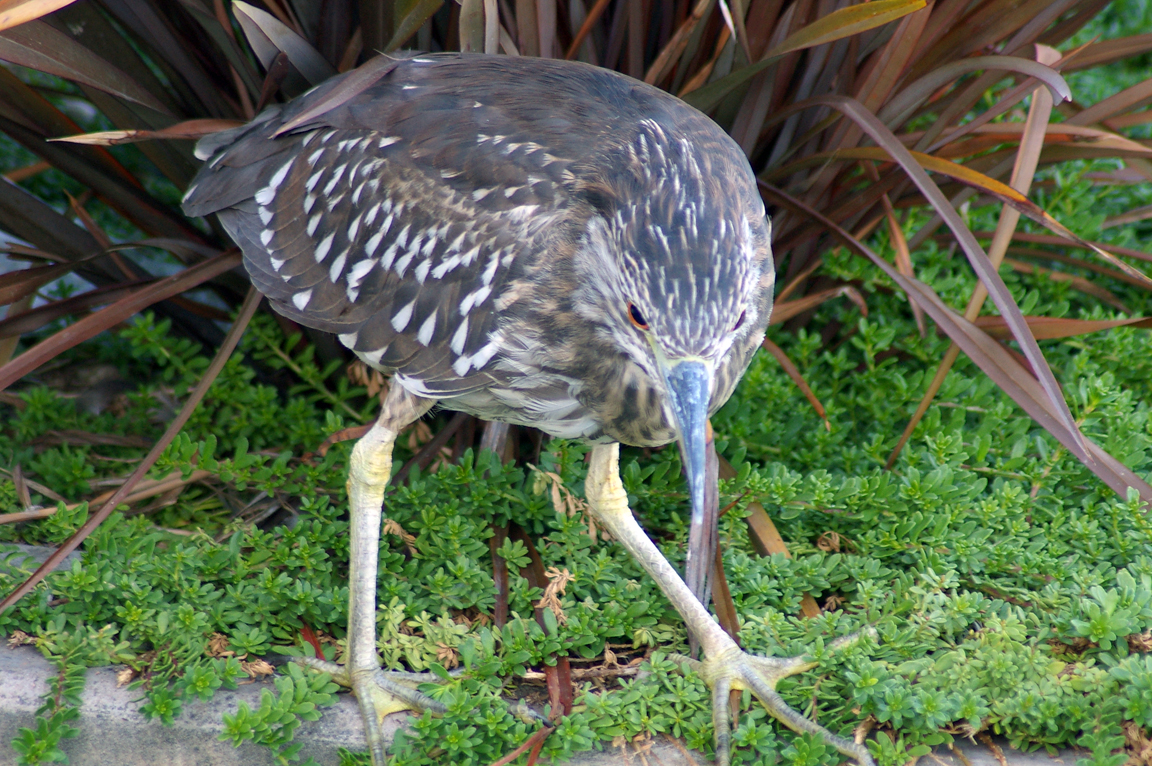
Immature
Striped brownish on neck and chest. Back brownish with buffy spots.
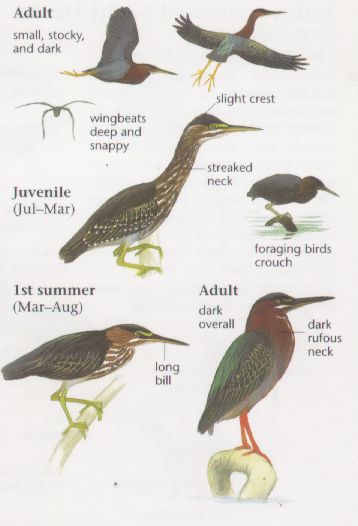
Photo taken from: The Sibley Field Guide by David Allen Sibley
© 2003 Cornell Lab of Ornithology
|
Habitat |
|
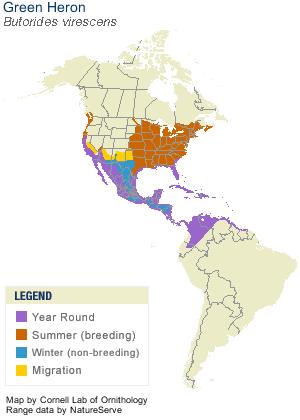
Breeds in swampy thickets. Forages in swamps, along creeks and streams, in marshes, ponds, lake edges, salt marshes, ponds and pastures. Winters mostly in coastal areas, especially mangrove swamps. |
|
Behavior |
|
Stands still next to water and grabs small fish with explosive dart of head and neck. One of the few birds that uses bait to attract fish, it drops such things as bread crusts, insects, and twigs onto the water. |
|
Food |
|
Small fish, invertebrates, insects, frogs, and other small animals. |
Taxonomy
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Ardeidae |
| Genus: | Butorides |
| Species: | Butorides virescens |
| Subspecies: | Butorides virescens anthonyi |
| Butorides virescens frazari | |
| Butorides virescens maculata | |
| Butorides virescens virescens |
Similar Species |
|
|
Bird Sound |
|
Flight or alarm call an explosive "skeow." Also make series of "kuk-kuk-kuk-kuk" notes. |
|
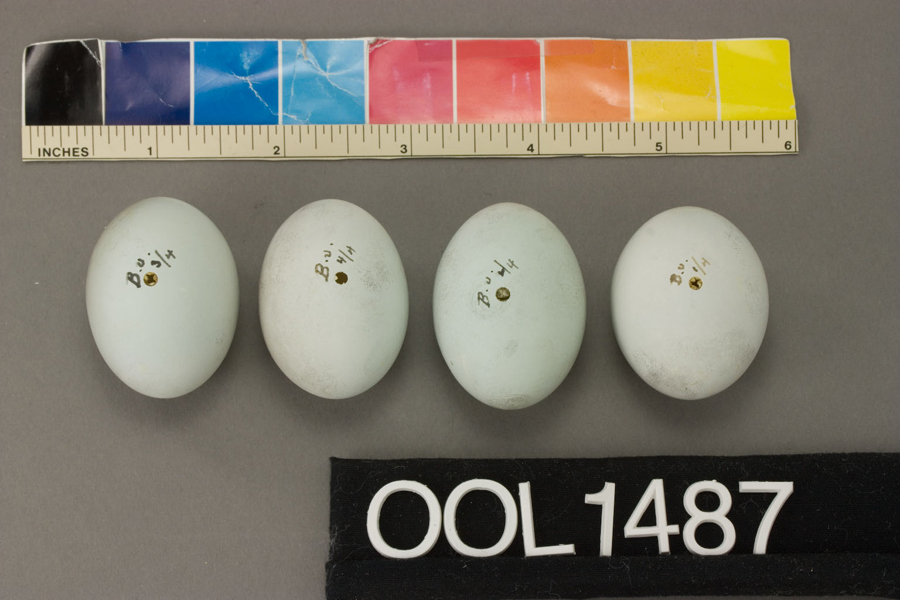
Eggs look like this |
|
Photo taken from: ARCTOS Collaborative Collection Management Solution |
|
Bird Sound |
|
Flight or alarm call an explosive "skeow." Also make series of "kuk-kuk-kuk-kuk" notes. |
Videos
GreenHeron 1
Juvenile in the Rain
GreenHeron 2
Adult in the Shore



































